Costochondritis is a common yet misunderstood condition that affects thousands of people throughout the world, causing chest pain and discomfort. Unfortunately, many medical practitioners are unfamiliar with this condition and it's often misdiagnosed or ignored entirely. In this blog post, we'll explore all the facts about costochondritis - from understanding symptoms to causes and treatments. With an expansive understanding of this condition, you'll be able to enter into conversations with medical professionals armed with the knowledge necessary for proper diagnosis and treatment.
What is Costochondritis?
Costochondritis is an inflammatory condition that affects the rib cage, specifically the cartilage connecting the ribs to the breastbone. This inflammation often leads to chest pain and discomfort in the chest area, although it can also radiate through to other areas such as the back or abdomen. The condition usually develops gradually over time but can also come on suddenly.
Symptoms of Costochondritis:
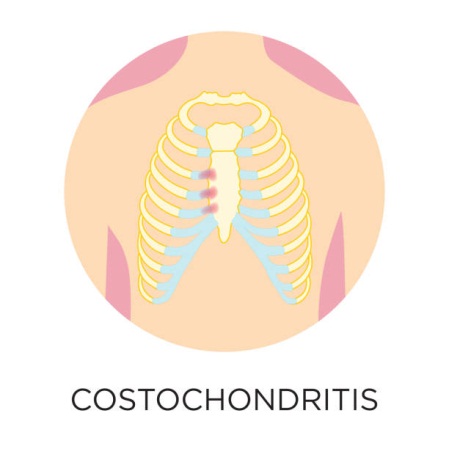
- Sharp or stabbing pain in the chest that may spread to other areas.
- Pain worsens with physical activity, coughing, and deep breathing .
- Tenderness when lightly squeezing the rib cage area.
- Swelling around the ribs.
- Muscle stiffness or soreness in the chest area.
- Limited range of motion due to pain and discomfort.
Causes of Costochondritis:
- Trauma or injury: Many cases of costochondritis are caused by direct trauma or injury to the chest area, such as a fall or car accident.
- Repetitive strain injuries: Repetitive activities like weightlifting, playing sports, or even prolonged coughing can lead to inflammation in the costal cartilage and cause costochondritis.
- Infectious diseases: Certain viral and bacterial infections can cause costochondritis, including tuberculosis, Epstein-Barr virus, and streptococcal infections.
- Medication side effects: Some medications, such as ibuprofen or prednisone, can trigger an inflammatory response in the chest area that causes costochondritis.
- Stress: Chronic stress, anxiety, and depression have been linked to an increased risk of developing costochondritis in some individuals.
- Other medical conditions: Certain types of arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis, can cause inflammation in the chest area that leads to costochondritis.
Diagnosis of Costochondritis:
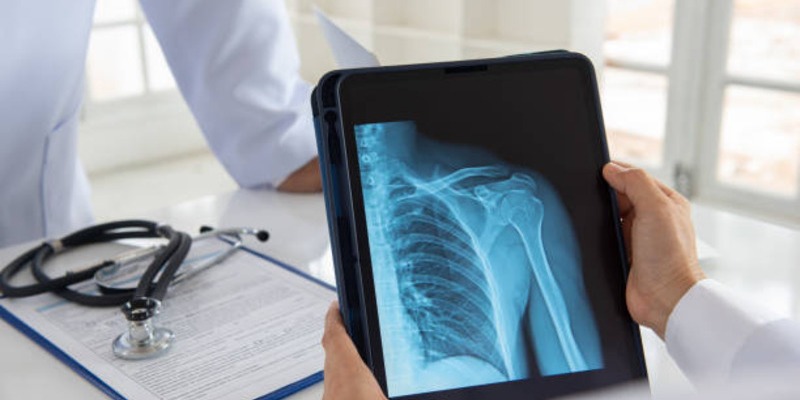
Diagnosing costochondritis primarily involves a physical examination by a healthcare provider. The doctor will likely press on your chest to identify areas of tenderness or swelling. This condition is typically diagnosed by ruling out other potential causes of chest pain. As costochondritis can mimic symptoms of a heart attack or other heart conditions, it's crucial to exclude these possibilities first.
There is no specific test for costochondritis, but additional diagnostic procedures may be recommended to rule out other conditions. These may include:
- Echocardiogram: This test uses sound waves to create pictures of your heart and its function, helping to rule out heart conditions.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): An ECG records the electrical activity of your heart and can help identify heart problems.
- Chest X-ray: A chest X-ray can help rule out other conditions that might cause chest pain, such as pneumonia or a rib fracture.
- CT or MRI scans: These detailed images can help identify any potential issues with your ribs or cartilage.
Treatment for Costochondritis:

Treatment for costochondritis primarily focuses on relieving pain and reducing inflammation in the affected area. The treatment strategy may differ from person to person, depending on the severity of symptoms and overall health condition. Here are some common treatments for costochondritis:
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain medications can alleviate the chest pain associated with costochondritis. It's important, however, to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new medication regimen.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapists can teach you exercises to stretch and strengthen the chest muscles, which can help reduce pain and prevent future episodes.
- Heat or Ice: Applying a hot or cold pack to the chest area can help alleviate pain.
- Rest and Avoidance of Physical Strain: Avoid heavy lifting or strenuous exercise, and get plenty of rest. This can allow the inflammation to decrease and prevent further strain on the chest area.
- Steroid Injections or Nerve Blocks: In severe cases, your doctor may recommend procedures to reduce inflammation and block pain signals.
Prevention of Costochondritis:
Although the exact cause of costochondritis is often unknown, there are several measures that can be taken to prevent or manage the condition:
- Exercise: Regular exercise, particularly those targeting chest muscles, can help strengthen the area and potentially decrease the risk of developing costochondritis. It's crucial to practice proper form and avoid unnecessary strain on the chest area during workouts.
- Stress Management: Since chronic stress and anxiety are linked to an increased risk of costochondritis, incorporating stress management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or yoga into your daily routine can help reduce this risk.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular sleep, can strengthen the immune system and potentially reduce the likelihood of infections that may trigger costochondritis.
- Avoiding Injuries: Care must be taken to avoid injuries to the chest area, especially during physical activities. Wearing protective gear during contact sports and practicing correct lifting techniques can minimize the risk of chest trauma.
Conclusion:
Costochondritis, while not life-threatening in itself, can cause significant discomfort and distress due to its chest pain symptoms. However, with a comprehensive understanding and proper management of this condition, individuals can lead a regular and active life. This involves a combination of medication, physical therapy, stress management, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Always consult with a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. Remember, every individual is unique, and what works best for one person may not work for another. Patience, persistence, and consistent adherence to treatment are crucial in managing costochondritis effectively.