Have you recently had a mammogram and been told you have an increased “fibroglandular density” (or high-density breast tissue)? Do you know what this means or why flagging it on your medical record is important? As a woman, having access to accurate and up-to-date information about our bodies can empower us to make everyday decisions for ourselves.
In this post, we are taking the time to discuss fibro glandular tissue – stressing the importance of understanding what it is, how it may impact you from a health standpoint, and providing clarity on its implications for detecting breast cancer.
Breast Tissue Types
Fibrous Tissue
Ligaments are a type of supporting or connective tissue that contains fibrous tissue. To retain the breast tissue in place, it extends from the chest wall to the skin.
Glandular Tissue
Glandular tissue includes the breast ducts and lobes, which produce milk during lactation.
Fatty Tissue
Fatty or greasy tissue largely gives the breast its shape and fills the areas between the glandular and fibrous tissue. It helps to cushion the breasts during activities such as running.
What is Fibroglandular Density
Fibroglandular density (or high-density breast tissue) is a naturally occurring part of the female anatomy, and it refers to the amount of glandular and connective (or fibrous) tissues present in the breasts.
On mammograms, these tissues appear as white areas. The degree of such density can range from low to high, with higher levels closely associated with an increased risk of breast cancer.
Although fibro glandular density is generally considered a benign (non-cancerous) factor, it can potentially make it more difficult to detect signs of any abnormal development in the breasts on a mammogram.
Also, women with higher levels of such density may be at a greater risk for developing breast cancer and require more frequent screenings. Therefore, it is important to be aware of the risks associated with high-density breast tissue and to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider.
On a mammogram, people with entirely fatty breasts or a few areas of dense tissue are classified as having low fibro glandular density (10-40%). Those with evenly dense tissue throughout or extremely dense tissue have high fibro glandular density (40-50%).
High fibro glandular density can make detecting abnormal breast development on a mammogram more difficult. It can also potentially increase the risk of developing breast cancer and require more frequent screenings.
It is important to be aware of the risks associated with high-density breast tissue and to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider. With access to accurate and up-to-date information, we can make informed decisions about our bodies and health.
Four Stages of Breast Density

When a mammogram is used to diagnose breast density, it’s classified into four stages. The stage depends on the amount of fatty and fibroglandular tissue in the breasts.
- Stage 0: Mostly fatty tissue with some scattered dense areas
- Stage 1: Heterogeneously dense (combination of both fatty and dense tissue)
- Stage 2: Extremely dense (predominately fibroglandular tissue)
- Stage 3: Almost entirely dense (fibro glandular tissue only)
Risk Factors for Fibroglandular Densities
High fibro glandular density can increase the risk of developing breast cancer and require more frequent screenings.
Certain factors put someone at a greater risk for having high levels of fibro glandular densities, including:
- Being pregnant or breastfeeding - these hormonal changes in the body can increase glandular tissue.
- Young age - women under the age of 40 tend to have higher levels of fibro glandular densities.
- Hormone replacement therapy - hormone replacement therapies can increase fatty and glandular tissues in the breast.
- Low body weight - people with lower body mass index (BMI) are more likely to have higher levels of fibro glandular density.
Screenings for Fibroglandular Density
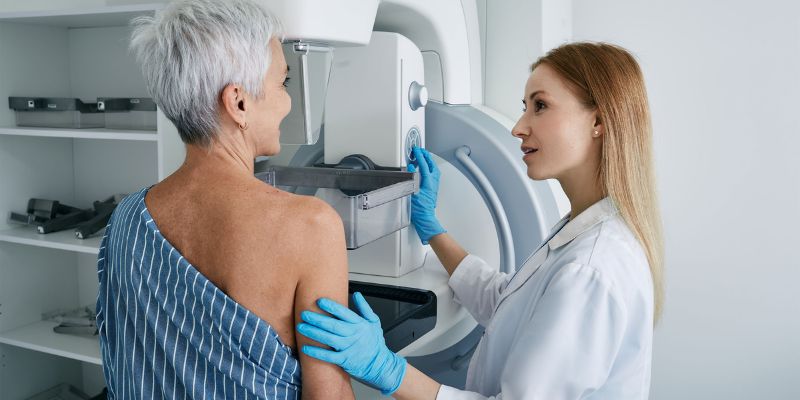
Fibroglandular density (or high-density breast tissue) is a naturally occurring part of the female anatomy. It raises the risk of breast cancer and can make detecting abnormal breast development on a mammogram more difficult. Therefore, it is important to understand fibro glandular density and its implications for detecting breast cancer.
To help identify fibro glandular density, healthcare professionals use a variety of screening tools. These include mammograms, breast ultrasounds, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, and biopsies.
Mammogram
Mammograms are X-ray pictures of the breasts used as the first-line screening for breast cancer. They can detect if someone has a dense breast tissue and identify high fibro glandular density.
Ultrasound
Sound waves are used in ultrasounds to provide an image of the breast. When a woman has dense breast tissue, an ultrasound is frequently advised because it can detect abnormal breast tissue that mammography could miss.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
An MRI scan uses magnets and radio waves to produce a detailed image of the breasts. It can detect breast cancer in people with high fibro glandular density that mammogram may miss, but it is more likely to produce false-positive results, leading to unnecessary testing.
Biopsy
If a healthcare provider detects an area of concern in the breast, they may do a biopsy to confirm or rule out cancer cells. A biopsy is a procedure where a small piece of breast tissue is removed and tested for cancer cells. There are three types of biopsies: Fine Needle Aspiration (FNA), Core Needle, and Open Biopsy.
A better understanding of fibro glandular density can help us make informed decisions about our health. If you are concerned that you may have high levels of fibro glandular densities, discussing your concerns with your healthcare provider is important. They will be able to identify any risk factors and recommend the appropriate screening and testing for you.
Preventing Fibroglandular Density
Certain lifestyle factors can increase the risk of developing fibro glandular density, and making some changes can help reduce this risk.
- Maintain a healthy weight - having an overweight or obese body mass index (BMI) is associated with higher levels of fibro glandular density.
- Avoid hormone replacement therapy - HRT can increase fatty and glandular tissues in the breast, leading to higher levels of fibro glandular density.
- Regular physical activity can help reduce fat in the body and increase lean muscle mass, both of which are associated with a lower risk for fibro glandular densities.
- Avoid alcohol - excessive drinking has been linked to higher levels of fibro glandular density.
Treatment for Fibroglandular Density
If a woman is diagnosed with high levels of fibro glandular density, treatments are available to help reduce the risk of developing breast cancer or other related health issues.
- Medication - Certain medications, such as tamoxifen or raloxifene, can help reduce the risk of developing breast cancer.
- Hormone therapy - For women with dense breasts due to hormone replacement therapy, discontinuing this medication may help reduce fibro glandular density over time.
- Surgery - In some cases, a doctor may recommend a lumpectomy or mastectomy to remove any abnormal, high-density areas in the breast.
FAQs
How serious is dense breast tissue?
Having dense breast tissue is not necessarily a cause for alarm, but it does mean that you should be aware of the increased risk of developing breast cancer. It’s important to discuss any concerns with your healthcare provider and follow their advice on screenings and treatments.
How can I lower my fibro glandular density?
Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding hormone replacement therapy, and engaging in regular physical activity can all help reduce the risk of developing fibro glandular density. Limiting alcohol consumption is also recommended.
What are the symptoms of dense breast tissue?
High levels of fibro glandular density cannot be felt by touch or seen on imaging tests. It’s important to discuss any concerns you may have with your healthcare provider. They can assess your risk factors and recommend screening tests if necessary.
Conclusion
Understanding fibro glandular density can help us make informed decisions about our health. Fibro glandular density is a naturally occurring part of the female anatomy, and it raises the risk of breast cancer and can make detecting abnormal breast development on a mammogram more difficult. Our healthcare providers use various screening tools to help identify fibro glandular density. Making lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of developing fibro glandular density. Talking to your healthcare provider is important if you are concerned that you may have high levels of fibro glandular densities.